About
There is an increasing demand for scientific support on climate-related decisions, in particular for providing societies and policy-makers with reliable and up-to-date information about atmospheric greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and natural sinks. The Global Carbon Project now reports annually on the evolution of global CO2 sources and sinks, their uncertainties and the resulting Global Carbon Budget, in phase with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) annual Conference of the Parties (COP).
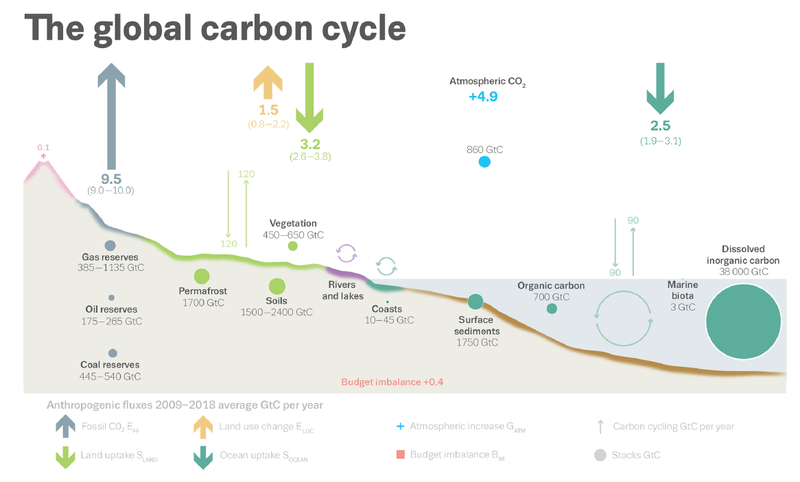
Figure 1: Perturbation of the global carbon cycle caused by anthropogenic activities, averaged globally for the decade 2009–2018 (GC/yr) (Friedlingstein et al., 2019, ESSD)
Global stocktaking, as defined by the Paris Agreement, further requires information about national GHG budgets that should be consistent with the global budgets and regularly updated. Still, the latest global carbon budget (Friedlingstein et al., 2019, ESSD) estimates a budget imbalance (knowledge-gap) of ca. 0.4 PgC (Figure). Top-down and bottom-up estimates also show important discrepancies over different latitudinal bands and a non-negligible fraction of the global carbon budget variability remains to be captured by land and ocean models. This underscores the need for regional studies to better use EO data and constrain key processes/regions in the global C-cycle.
The aims of the international initiative ‘REgional Carbon Cycle Assessment and Processes’, Phase 2 (RECCAP-2) coordinated by the Global Carbon Project are to collect and synthesize regional data for 14 large regions of the globe with a requirement of harmonization sufficient to be able to scale these budgets to the globe and to compare different regions. Key policy-relevant challenges for the scientific community and objectives of the RECCAP-2 project are to:
- Improve quantification of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and their sources;
- Develop robust observation-based estimates of changes in carbon storage and greenhouse gas emissions and sinks by the oceans and terrestrial ecosystems, distinguishing whenever possible anthropogenic vs. natural fluxes and their driving processes;
- Gain science-based evidence of the response of marine and terrestrial regional GHG budgets to climate change and direct anthropogenic drivers.
To address these objectives, RECCAP-2 will update a set of global syntheses and regional GHG budgets of all land and ocean regions that were only collected for the period 2000-2009 in the first phase RECCAP1, and explore mechanisms to deliver by 2022 an assessment based on scientific evidence, considering uncertainties, understanding of drivers, and retrospective analysis of recent trends.
The topics to be explored within RECCAP-2 are:
- Regional budgets and drivers. Focus on the last decade (2009-2020) and redo previous decades for trends and (sub-)decadal variability analysis. 14 regions globally for land; 5 for oceans divided as interest/data availability. Large countries will have their own GHG budget (e.g., Australia, China, EU, India, Russia, USA) given its higher policy relevance.
- Regional hotspots and drivers (including acceleration of change, tipping points).
- Trends (multi-decadal) and variability (annual to decadal) of change of major GHG fluxes.
- Improve incorporation of freshwater and coastal zone fluxes within both land and ocean budgets.
- Global stocktake and tracking towards net zero emissions (anthropogenic versus all fluxes).
- Reconcile and constrain the global GHGs budget with the aggregation of regional budgets (e.g. resolving tropical vs. northern hemisphere net land carbon sink).
The scale of the RECCAP-2 regional analysis will have increased detail compared to those in RECCAP-1. The analysis will also focus on spatially explicit maps of monthly CO2 fluxes from TRENDY, data driven models and from inversions
ESA-CCI for RECCAP-2
This project aims to support, in cooperation with the GCP, the scientific synthesis and assessment activities of regional carbon budgets and their drivers of the new RECCAP-2 initiative by making use of EO-data and regional cuts of annually updated global terrestrial and ocean carbon models, and atmospheric CO2 inversions, taking stock of new satellite-based surface monitoring products of climate and ecological variables now available within the framework of ESA-CCI.
The data-streams used in ESA-CCI RECCAP-2 are:
- Atmospheric inversions of concentration measurements based on surface in situ networks and satellite remote sensing, with “high resolution” inversions
- Output from process-based terrestrial ecosystem models these models being driven by climate fields and land cover change
- Output of “data-driven” bottom-up approach machine learning methods using satellite data and climate fields
- These three approaches are largely independent; even though inversions use as prior the output from process-based models, they usually do not use specifically the TRENDY models’ output. TRENDY models and data-driven models also share climate forcing as input.
Objective
The goal of the ESA-CCI project RECCAP-2 is to support and accelerate the analysis of regional carbon budgets based on the results of data-driven models and process-oriented Global Dynamic Vegetation Models used by the Global Carbon Project by operationalizing the production and uncertainty assessment of regional CO2 budgets, taking stock of newly available land surface and atmospheric remote sensing data to constrain and improve model results. The RECCAP-2 project specifically aims to:
- Provide higher spatial resolution and annual updates for the global and regional carbon balance with the aim of improving the quantification and understanding of drivers, processes and hot spot regions essential for predicting the future evolution of any carbon-climate feedback
- Build on the experience from the RECCAP analysis from 2009-2012 to address the growing demand for the capacity to measure, report on, and verify the evolution of regional fluxes and the outcomes of climate mitigation policies;
- Respond to the demand of ESA and other space agencies for the better appropriation and effective use of remote sensing products in climate science. Here specifically, we will use a variety of remote sensing products to directly constrain carbon fluxes in data-driven models, and to be used as input or to evaluate process-based ecosystem models.
- Evaluate the potential of ESA-CCI and other earth-observation data to track country-level natural and anthropogenic GHG fluxes, to support the reporting by National Agencies in the UNFCCC global stocktake process.
Phase 1
The first phase of the project (2018-2020) was based on CO2 fluxes data-streams from three different approaches and delivered annual updates of land-atmosphere CO2 fluxes at global and regional scales (Tier 1), consistent with the global carbon budget assessment from the Global Carbon Project (GCP) and with regional details in space and time to analyse the underlying drivers (Tier 2, Figure 2 below).
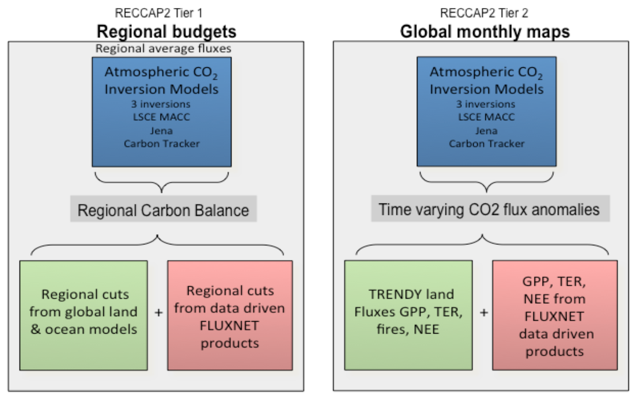
Figure 2: Approaches to global and regional scale land-atmosphere CO2 fluxes.
Phase 2
The second phase of ESA-CCI RECCAP2 (2020-2022) aims to build on the results from Phase 1 to demonstrate the feasibility of the RECCAP2 approach to contribute to the global stocktake process with national-scale GHG budgets, in collaboration with national inventory agencies. The main objectives of Phase 2 are:
- To evaluate the feasibility of producing at least every two years updated estimates of GHG balance anomalies (natural and anthropogenic) at country level constrained by EO data using ensembles of top-down atmospheric inversions and bottom-up land surface models;
- To improve the consistency between estimates of greenhouse budgets produced against official estimates of national anthropogenic emissions and land fluxes in the Land Use and Land Use Change and Forestry sector (LULUCF) produced by countries and reported to the UNFCCC as national communications;
- To promote a dialogue with selected national inventory agencies to identify the largest sources of uncertainties in inventories and how the uncertainty provided by ESA-CCI datasets can support uncertainty estimation; A special focus will be given to the comparison between research-based estimates of GHG budgets for CO2, N2O and CH4 with national GHG inventories regularly reported by countries to the UNFCCC for the UK, Germany, France, Italy, Columbia and Brazil
- To scope the information that could be delivered by EO data products and priority requirements for data products that would help to improve national inventories.
Data
The following data is available from the RECCAP-2 project.
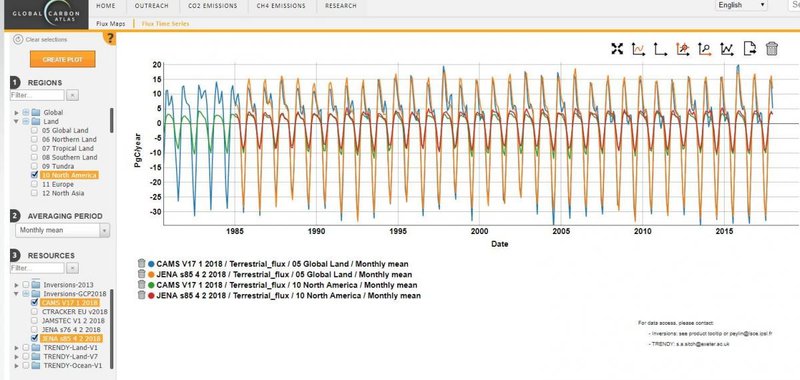
The Global Carbon Atlas allows for quick time-series and map visualisation of the carbon fluxes from the datasets used in RECCAP-2.
The Global Carbon Atlas is an online platform to explore, visualize and interpret global and regional carbon data arising from both human activities and natural processes. The graphics and data sources are made available in the belief that their wide dissemination will lead to new knowledge and better-informed decisions to limit and cope with human-induced climate change. The Global Carbon Atlas is a community effort under the umbrella of the Global Carbon Project based on the contributions of many research institutions and individual scientists around the world who make available observations, models, and interpretation skills.
The land-surface CO2 fluxes from the five inversions and 14 dynamic global vegetation models from GCB2018 (Le Quéré et al. 2018) can now be explored in the Global Carbon Atlas:
For data access, please contact:
- Inversions: see product tooltip or peylin@lsce.ipsl.fr
- TRENDY: s.a.sitch@exeter.ac.uk
Team
The RECCAP-2 consortium is based on a close collaboration between the following partners:
- Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement, France
- University of Exeter, United Kingdom
- Max-Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry, Germany
- Global Carbon Project via Future Earth, Sweden
Publications
Click on the following links for publications relating to the RECCAP-2 project.
Scaling carbon fluxes from eddy covariance sites to globe: synthesis and evaluation of the FLUXCOM approach (M. Jung et al.)
Sources of Uncertainty in Regional and Global Terrestrial CO2 Exchange Estimates (A. Bastos, et al.)
Friedlingstein, P., Jones, M. W., O'Sullivan, M., Andrew, R. M., Hauck, J., Peters, G. P., et al. (2019). Global Carbon Budget 2019. Earth System Science Data, 11(4), 1783–1838. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-11-1783-2019
IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land
ESA-CCI RECCAP-2 (M. O'Sullivan and A. Bastos) contributed to the IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land Chapters 1 and 2 with regional estimates of natural sinks and land-use change emissions.
This article is part of a Special Issue ‘The impact of the 2015/2016 El Niño on the terrestrial tropical carbon cycle: patterns, mechanisms and implications’.
News and events
Contacts
The following people can be contacted within the RECCAP-2 project.
Science Leaders:
- Philippe Ciais – philippe.ciais@lsce.ipsl.fr
- Ana Bastos – ana.bastos@lmu.de
ESA Technical Officers:
- Clement Albergel – clement.albergel@esa.int
Latest news & events

Working for ESA: procurement and proposal submission process
An Introduction to ESA Star - ESA's System for Tendering and Registration
Mehr erfahren
Climate Change & Cities: Open Competitive Tenders Launched
Two New City Research Calls On Urban Resilience To Climate Change Using Earth Observation Data
Mehr erfahren
Record Rise In Methane Emissions Linked To Wetlands Flooding
Study Reveals Surge In Wetland Methane Emissions Aligning With Rising Groundwater, La Niña And Regional Warming
Mehr erfahren
Highlighting Earth Observation data across COP29
ESA participation in plenary sessions, side events and panel discussions
Mehr erfahren
ESA at COP29
ESA is participating in COP29 to highlighting satellites' role in tackling climate change
Mehr erfahren

Open Competitive Tender for CLIMATE-SPACE Knowledge Exchange
ESA Tender Action Number: 1-12141. ESA Activity Number: 1000039650.
Mehr erfahren
Little Pictures winner announced at COP28
Results of Europe-wide climate data visualisation showcased
Mehr erfahren
New Tender: CROSS-ECV ACTIVITIES Tender Action Number: 1-12062
New tender issued by the ESA Climate Office (Activity Number: 1000039196)
Mehr erfahren
Harnessing Earth Observation for Climate Action
ESA in conversation Prof Jim Skea with IPCC Chair during the COP28 Earth Information day
Mehr erfahren
COP28: ESA Climate Office events
The Climate Office is contributing to several events at COP28, UAE, Dubai
Mehr erfahren
Taking climate action with Earth observation
Satellites' contribution to understanding climate change and supporting climate action are under the COP28 spotlight
Mehr erfahren



